The mechanism of action of Clexane® is primarily through the activation of antithrombin [38], a molecule synthesised in the liver that plays a central role within the human haemostasis system through regulating appropriate wound healing [42].
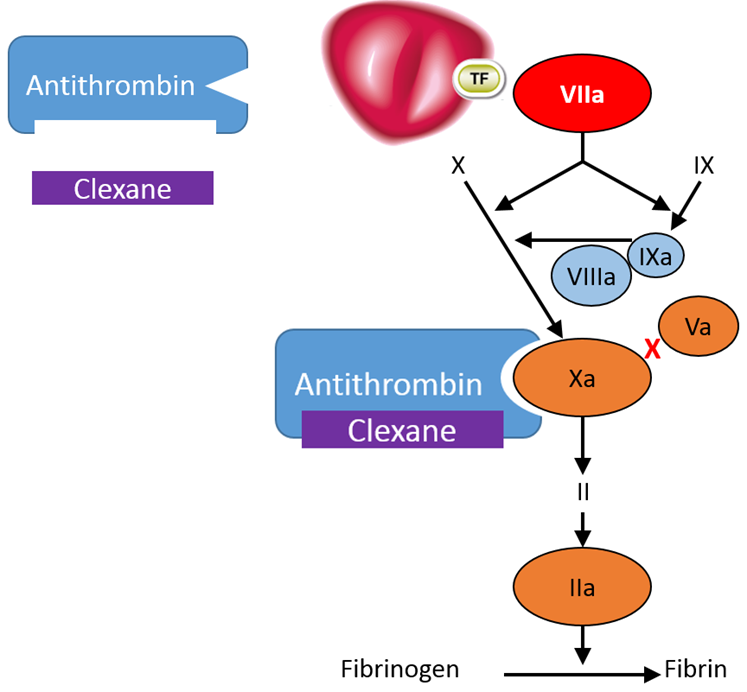
Clexane® forms a complex with antithrombin. This complex undergoes a conformational change; in its altered conformation, the complex inhibits FXa, which is the primary mechanism of action.