A stroke is the result of a disturbance of the blood supply to the brain. This happens because an artery is blocked by a blood clot, called an ‘ischaemic’ stroke, or if a blood vessel bleeds in the brain, called a ‘haemorrhagic’ stroke.
The consequences of an arterial obstruction depend on which part of the brain is denied oxygen by the affected blood vessel. They may include speech, swallowing and vision impairment as well as paralysis of one side of the body or partial paralysis. These functional disturbances of the brain are resolved with great difficulty over a long period of time or are never fully resolved. It is important to seek immediate medical attention to restore normal blood flow as soon as possible and to prevent the most serious complications of this type occurring which could include death.
Symptoms
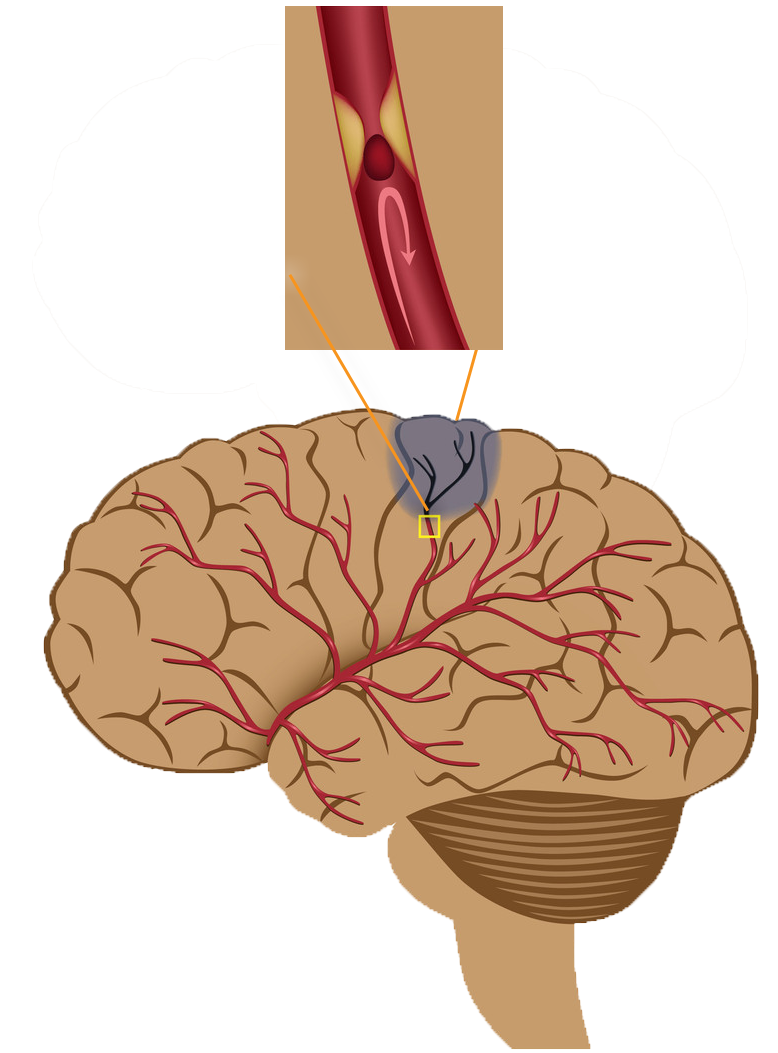
The figure shows the blockage of arterial blood supply by a blood clot.