Clexane® is an anticoagulant of the low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) class, derived from natural porcine heparin and with a wide spectrum of licenced indications.
Enoxaparin is marketed in the Republic of Ireland under the trade name Clexane®. As a LMWH, Clexane® comprises a fragment of the naturally occurring mucopolysaccharide, heparin. It has a variable size, with an average molecular weight of 4–5 kilodaltons (kD) [38].
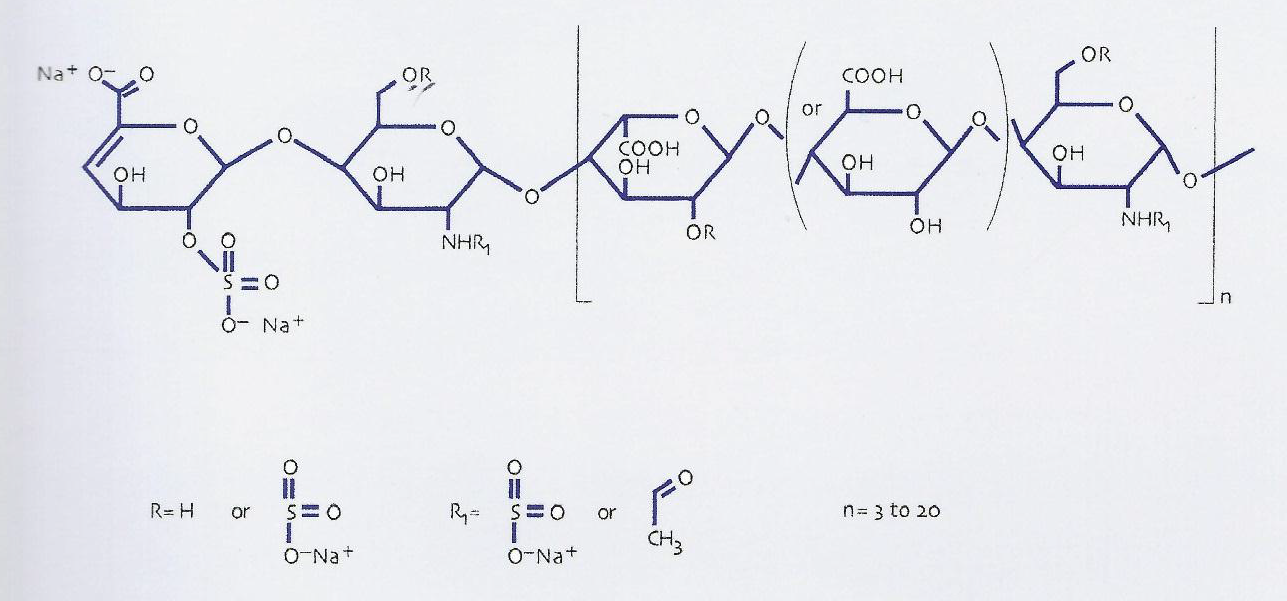
Figure: molecular structure of Clexane®
Clexane® exerts its anticoagulant effect by preventing the formation of blood clots through binding to antithrombin, a naturally occurring coagulation inhibitor and potentiating its action. Antithrombin is a natural inhibitor of the coagulation factors FXIa, FIXa, FXa and FIIa (thrombin) [38].
The pharmacodynamic profile of enoxaparin, like other LMWHs, has advantages over unfractionated heparin (UFH). These include:
- Minimal plasma binding, leading to more reliable anticoagulant effects and eliminating the need for therapeutic monitoring
- A greater capacity to release tissue factor pathway inhibitor and hence the generation of FVIIa
- A lower propensity to inhibit platelet aggregation
- Less inhibition by platelet factor 4
- Potential antiplatelet effects via higher degrees of suppression of von Willebrand factor
- Less propensity to cause heparin-induced thrombocytopenia and osteoporosis
Therapeutic indications
In the Republic of Ireland, Clexane® has a wide range of therapeutic indications. Please check medicines.ie [39]:
Clexane is indicated in adults for:
- Prophylaxis of venous thromboembolic disease in moderate and high risk surgical patients, in particular those undergoing orthopaedic or general surgery including cancer surgery.
- Prophylaxis of venous thromboembolic disease in medical patients with an acute illness (such as acute heart failure, respiratory insufficiency, severe infections or rheumatic diseases) and reduced mobility at increased risk of venous thromboembolism.
- Treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE), excluding PE likely to require thrombolytic therapy or surgery.
- Prevention of thrombus formation in extra corporeal circulation during haemodialysis.
- Acute coronary syndrome:
- Treatment of unstable angina and Non ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI), in combination with oral acetylsalicylic acid.
- Treatment of acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) including patients to be managed medically or with subsequent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
Contraindications
Enoxaparin sodium is contraindicated in patients with:
- Hypersensitivity to enoxaparin sodium, heparin or its derivatives, including other low molecular weight heparins (LMWH) or to any of the excipients listed in section 6.1 of the SmPC;
- History of immune mediated heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) within the past 100 days or in the presence of circulating antibodies;
- Active clinically significant bleeding and conditions with a high risk of haemorrhage, including recent haemorrhagic stroke, gastrointestinal ulcer, presence of malignant neoplasm at high risk of bleeding, recent brain,spinal or ophthalmic surgery, known or suspected oesophageal varices, arteriovenous malformations, vascular aneurysms or major intraspinal or intracerebral vascular abnormalities;
- Spinal or epidural anaesthesia or loco-regional anaesthesia when enoxaparin sodium is used for treatment in the previous 24 hours.
Posology and administration
Different dosages of Clexane® are recommended for the various therapeutic indications [39]. Clexane (enoxaparin) is available as convenient colour-coded pre-filled syringes.
To identify the corresponding syringe. When using Clexane, colour alone should not be used to distinguish syringes – always read labels carefully.

Further information is available in the SPC.